🔗 Official Website
Trends
Description
Brain2Music is amazing project.
The process of reconstructing experiences from human brain activity offers a unique lens into how the brain interprets and represents the world. In this paper, we introduce a method for reconstructing music from brain activity, captured using functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI). Our approach uses either music retrieval or the MusicLM music generation model conditioned on embeddings derived from fMRI data. The generated music resembles the musical stimuli that human subjects experienced, with respect to semantic properties like genre, instrumentation, and mood. We investigate the relationship between different components of MusicLM and brain activity through a voxel-wise encoding modeling analysis. Furthermore, we discuss which brain regions represent information derived from purely textual descriptions of music stimuli.
The project was developed by a research team from Google, Osaka University, NICT and Araya Inc. It can read the characteristics of the "type", "instrument arrangement" and "mood" of the music being auditioned from the brain response, and generate music based on these characteristics. For example, if the auditioned music is jazz, the generated music will also have elements of jazz.

This research is expected to deepen our understanding of the relationship between music and the brain, and may one day reconstruct music from the human imagination. They used functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) to capture brain activity, and music retrieval or the MusicLM music generation model to generate music. The generated music resembles musical stimuli experienced by human subjects in terms of semantic properties such as genre, instrument, and mood.
Their method consists of the following steps:
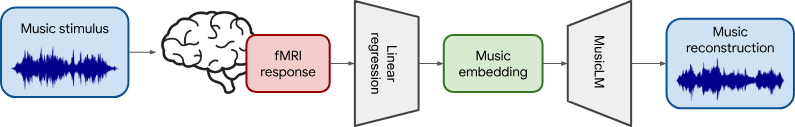
- 1. Brain activity data acquired through functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI). This data is then compressed or transformed into a model called "MuLan". MuLan is a music language model that can represent music as a 128-dimensional vector (that is, a list containing 128 elements). Each dimension represents a certain characteristic of music, such as rhythm, melody, harmony, etc.
- 2. Subsequently, the music generative model MusicLM is conditioned to generate music reconstructions, and the generated music is designed to resemble as closely as possible the original stimulus, that is, the activity in the human brain when listening to music. In addition to generating new music, they also considered another method, which is to find the music that best matches the brain activity from a large existing music database.
- 3. They also found that two components of MusicLM (MuLan and w2v-BERT) have a certain correspondence with human brain activity in the auditory cortex. In addition, they found that the brain regions involved in extracting information from text and music overlapped.
Features and Benefits
- 1. Brain activity data acquired through functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI). This data is then compressed or transformed into a model called "MuLan". MuLan is a music language model that can represent music as a 128-dimensional vector (that is, a list containing 128 elements). Each dimension represents a certain characteristic of music, such as rhythm, melody, harmony, etc.
- 2. Subsequently, the music generative model MusicLM is conditioned to generate music reconstructions, and the generated music is designed to resemble as closely as possible the original stimulus, that is, the activity in the human brain when listening to music. In addition to generating new music, they also considered another method, which is to find the music that best matches the brain activity from a large existing music database.
- 3. They also found that two components of MusicLM (MuLan and w2v-BERT) have a certain correspondence with human brain activity in the auditory cortex. In addition, they found that the brain regions involved in extracting information from text and music overlapped.
Open Source
Tags
Compare with other popular AI Tools
Compare with Voicemod-Free Real-Time Voice Changer for PC & Mac
Compare with Murf.ai-Text to Speech Software
Compare with D-ID AI Video Generator
Compare with Notta-Transcribe Audio to Text
Compare with Fliki.ai-Text to Video and Text to Speech
Compare with Play.ht-AI Voice Generator with 600+
Compare with HitPaw AI Video Enhancer
Compare with Lalal.ai-Vocal Remover & Instrumental AI Splitter
Compare with Captions.ai-Your AI-powered Creative Studio